What is a Consumer Health Company? Riffing Off of Deloitte’s Report on CHCs/A 2Q2025 Look at Self-Care Futures

The health care landscape in 2030 will feature an expanded consumer health industry that will become, “an established branch of the health ecosystem focused on promoting health, preventing, disease, treating symptoms and extending healthy longevity,” according to a report published by Deloitte in September 2024, Accelerating the future: The rise of a dynamic consumer health market. While this report hit the virtual bookshelf about six months ago, I am revisiting it on this first day of the second quarter of 2025 because of its salience in this moment of uncertainties across our professional and personal lives — particularly related to
Health Care Nation – How to Inspire a Rosa Parks Moment for Healthcare in America?

Tom Lawry may be best-known as a leading voice on AI in health care; after all, he’s written two very well-selling books on the topic, speaks all over the world on the subject, and in his most recent company-based gig helped lead Microsoft’s efforts in AI in health care and life sciences. When his publisher asked him to write a third book on AI in health care – still a hot topic in publishing – Tom said he’d rather turn to a subject long on his mind: the state of health care in America and how to change the conversation
The New “Paging Dr. Google?” DTC-AI for Health Care

While most people in the U.S. who have used large language models (like ChatGPT) for informal learning, entertainment, and getting information about products and services, 39% of U.S. adults have also tapped into LLMs to source information about physical or mental health. This insight is brought to us in the brilliantly titled report, Close encounters of the AI kind, from the Imagining the Digital Future Center at Elon University. The principle author of the survey report is the Center’s Director, Lee Rainie, whose name many of you will know from his two+ decade career at the Pew Research Center (and
The Top Patient Safety Risks in 2025 Are Mostly About the “Human OS” – Reading ECRI’s Annual Report

Each year, ECRI (the ECRI Institute) publishes an annual report on the Top 10 Patient Safety Concerns for the year. The 2025 list was published today. My read of it is that most of these risks have to do with what I’ve been referring to as the Human OS, the Human Operating System, in my talks and teachings. In this post, I’ll focus on 2 of the 10 most top-of-mind in my current workflow with clients and speaking: #1 and #3. Here’s the list of 10, calling out: Risks of dismissing
How Tariffs Could Wreak Havoc on Health Care Costs and Supply Chains in the U.S.

Non-clinical goods and services can comprise $1 in $5 of net patient revenue in the U.S. health care economy, research from LogicSource gauges. The possible tariffs proposed by the next U.S. President could drive those costs up, eroding financial margins in many parts of American health care — from hospitals to drug companies and med-tech innovators. Simply put, “President-elect Donald Trump’s pledge to enact across-the-board tariffs isn’t going over well in the health care industry,” POLITICO reported. Why worry about tariffs’ impacts on health care? Ask the CFO of Reckitt, Shannon Eisenhardt, who spoke
Americans’ Views on the Quality of Healthcare Fell to a Record Low — with Costs Ranking as the Most Urgent Problem for Health in the U.S.

Americans’ perception of the quality of health care in the U.S. fell to the lowest level since 2001, Gallup found in a poll of U.S. health citizens’ views on health care quality, published December 6, 2024. In 2024, only 44% of Americans said that the quality of health care int he U.S. was excellent or good — conversely, 56% of Americans though health care quality was only fair or poor. By political party, that included 50% of Democrats evaluating the quality of care highly compared with 42% of Republicans. Only 28% of people in
3 in 4 U.S. Patients Say the Healthcare System is Broken — But Technology Can Help

Patients “yearn” for personalized services and relationships in health care — optimistic that technology can help deliver on that hope — we learn in Healthcare’s Future: Balancing Progress and Perception, a health consumer survey report from Lavidge. Lavidge, a communications/PR/marketing consultancy, polled U.S. patients’ attitudes about health care and technology in June 2024, publishing the report earlier this month. Start with over-arching finding that, “Three out of four patients believe the U.S. healthcare system is broken and there is a strong sense of distrust,” Lavidge asserts right at the top of
Americans Want More Health Care Issues Baked into the 2024 Elections – Gallup

Beyond women’s health and abortion politics, most Americans are looking for more health care baked into the 2024 Elections, based on a new poll from Gallup in collaboration with West Health. Two in three U.S. adults thought health care was not receiving enough attention during the 2024 Presidential campaign as of September 2024. This is a majority shared opinion for voters across the three party IDs in the U.S., shown in the first bar graph. The research polled 3,660 U.S. adults in September, about two-thirds before the presidential debate held September 10, and about one-third
On This July 4th 2024, Let’s Remember the Doctors Who Have Helped Patients Declare Their Independence – Wisdom from Michael Millenson

“’A reform,’ wrote a 19th-century British parliamentarian, ‘is a correction of abuses. A revolution is a transfer of power. As we celebrate the American Revolution, catalyzed by men who broke ranks with their peers to overthrow a power structure that seemed immutable, let’s also celebrate those physicians who broke with their peers and declared independence for American patients.” So begins an informative, timely essay on participatory medicine and patient engagement researched and beautifully written by Michael Millenson, whom I am blessed to call both dear friend and professional colleague. Michael’s essay on the
Can AI Help to Improve Health Equity? U.S. Scientists Weigh In With “Yes,” Baking in Ethics and Accountability

The Federation of American Scientists (FAS) was founded in 1945 by a group of scientists concerned about the atomic bomb — sharing a mission to focus on technology, science, and innovation to, in the Association’s words, “work toward a safer, more equitable, and more peaceful world.” Nearly 80 years after the organization’s launch, the FAS is focusing on the growing role of artificial and augmented intelligence across the many areas that touch peoples’ lives — including health care and well-being. The FAS published a state-of-the-nation essay on June 27 on Improving Health Equity Through AI.
“Listen to Me:” Personalization in Health Care Starts With Taking Patients’ Voices Seriously – the 15th Beryl Institute-Ipsos PX Pulse Survey

Patients’ experience with health care in the U.S. dropped to its lowest point over the past year, explained in the 15th release of The Beryl Institute – Ipsos PX Pulse survey. The study into U.S. adult consumers’ perspectives defined “patient experience” (PX) as, “The sum of all interactions, shaped by an organization’s culture, that influence patient perceptions across the continuum of care.” The survey was fielded by Ipsos among 1,018 U.S. adults in March 2024. Health care providers (and other industry stakeholders that go B2B or B2B2C (or P) are all thinking
A Health Consumer Bill of Rights: Assuring Affordability, Access, Autonomy, and Equity
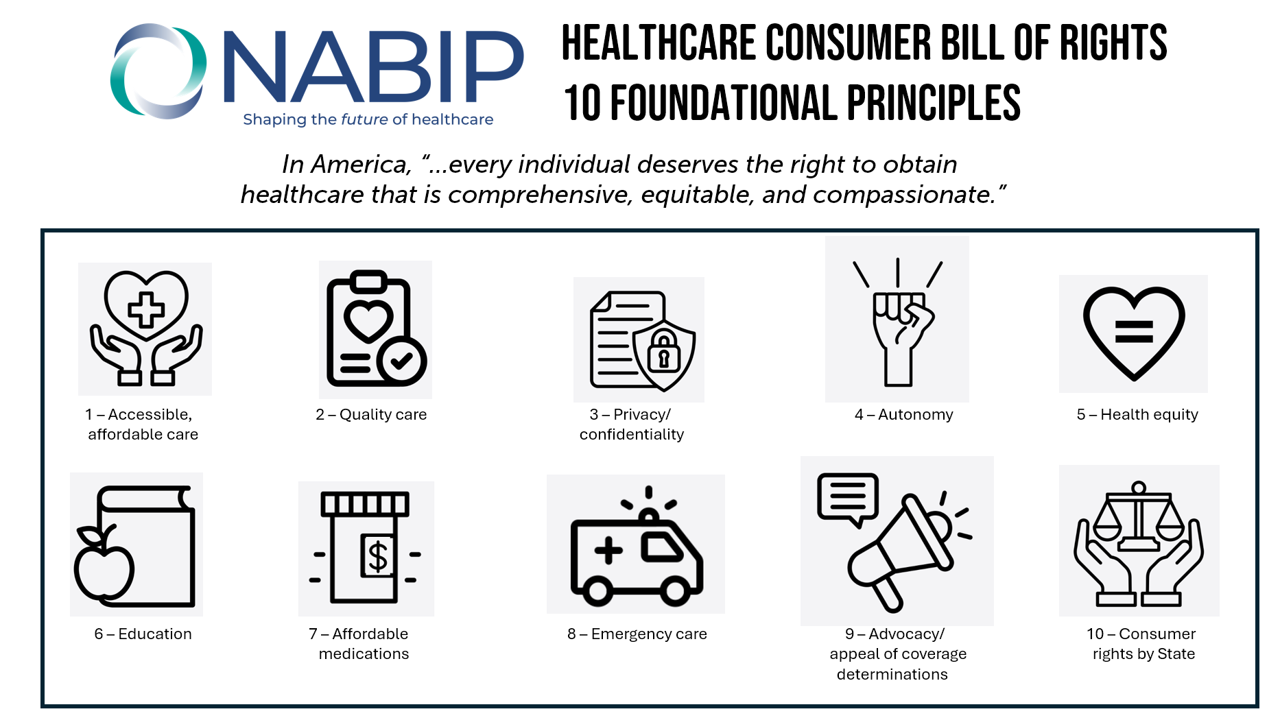
Let’s put “health” back into the U.S. health care system. That’s the mantra coming out of this week’s annual Capitol Conference convened by the National Association of Benefits and Insurance Professionals (NABIP). (FYI you might know of NABIP by its former acronym, NAHU, the National Association of Health Underwriters). NABIP, whose members represent professionals in the health insurance benefits industry, drafted and adopted a new American Healthcare Consumer Bill of Rights launched at the meeting. While the digital health stakeholder community is convening this week at VIVE in Los Angeles to share innovations in health tech, NABIP
Nurses Earn Highest Grade for Care Far Above All Other Health Care Workers — Including Doctors — In Latest Gallup Poll
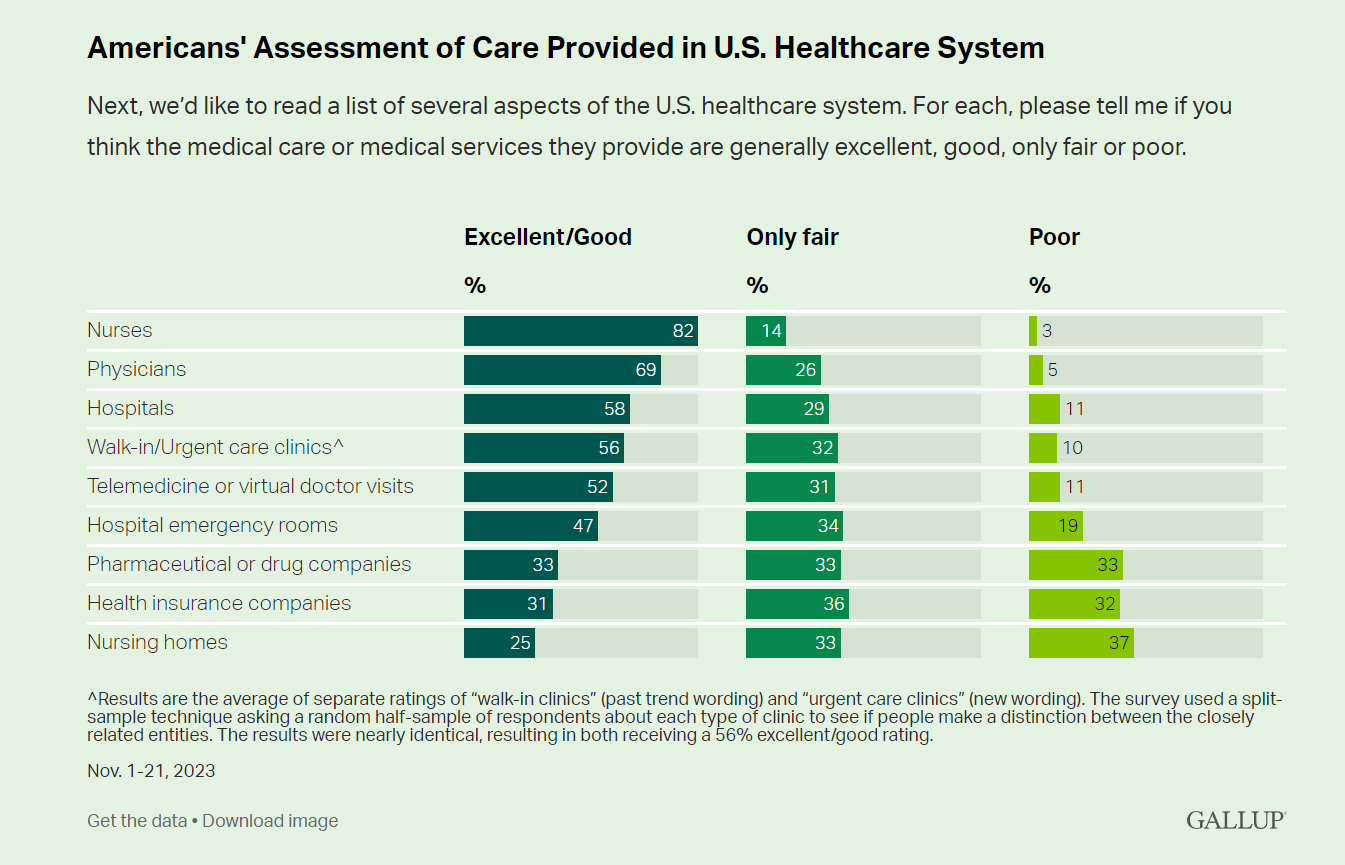
Nurses rank highest among various factors in the U.S. health system in the latest Gallup poll — earning a grade of “excellent” or “good” by American adults surveyed in November 2023. Further substantiation for nurses’ topping this poll of excellent care is that Gallup found historic low confidence in the U.S. health system among Americans earlier this year in a July study. Note that 8 in 10 consumers rate nurses excellent/good compared with 7 in 10 people ranking physicians this way, 6 in 10 for hospitals, 5 in 10 for telemedicine/virtual visits, and
There’s a New “O” in Medicine-Town – Welcome OPill to the Front of the Counter

You may not be able to get that ear-worm jingle that goes “O O O Ozempic” out of your musical mind, but I’m happy to tell you there’s a new “O” in town: the Opill. Welcome to the first OTC contraceptive for sale in the USA. I wrote about Perrigo’s Opill here in Health Populi in May 2023 as a “signpost on the road to retail health.” It’s official: “The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Opill®, a progestin-only daily oral contraceptive, for over-the-counter (OTC) use for all ages.
The Top 10 Patient Safety Concerns for 2023 Are About Social, Mental and Behavioral Health

Ten years ago, ECRI named the top 10 health technology hazards for 2013: they were alarm hazards, medication administrative errors using infusion pumps, unnecessary exposure and radiation burns from diagnostic radiology procedures, patient/data mismatches in EHRs and other HIT systems, interoperability failures with medical devices and health IT systems, and five other tech-related hazards. In 2014, ECRI pivoted the title of this annual report to “patient safety concerns,” a nuance away from health technology. Fast forward to 2023 and ECRI’s latest take on the Top 10 Patient Safety Concerns 2023. While technology is embedded in this list, the headlines have more
The Patient As the Payer: Self-Pay, Bad Debt, and the Erosion of Hospital Finances
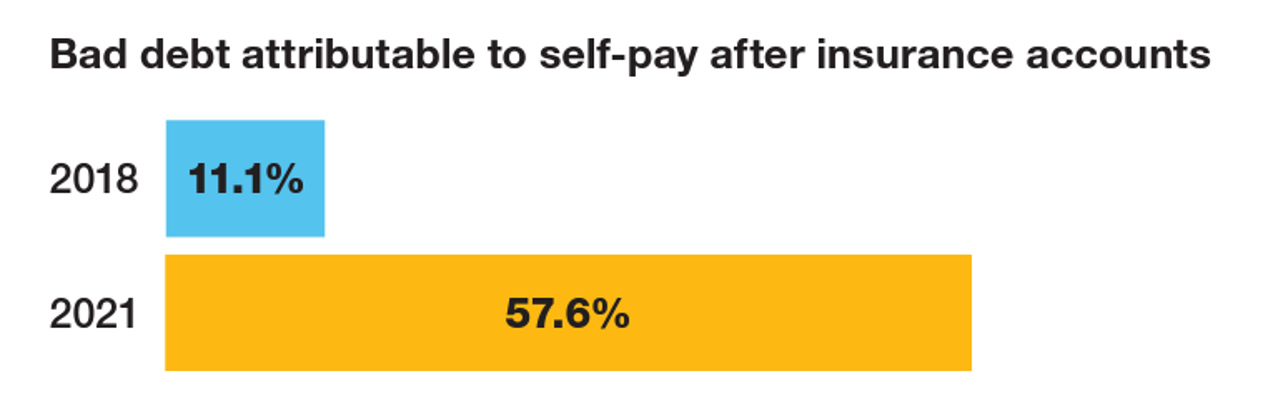
“The odds are against hospitals collecting patient balances greater than $7,500,” the report analyzing Hospital collection rates for self-pay patient accounts from Crowe concludes. Crowe benchmarked data from 1,600 hospitals and over 100,00 physicians in the U.S. to reveal trends on health care providers’ ability to collect patient service revenue. And bad debt — write-offs that come out of uncollected patient bill balances after “significant collection efforts” by hospitals and doctors — is challenging their already-thin or negative financial margins. The first chart quantifies that bad debt attributable to patients’ self-pay payments
The 2022 US Health System Report Card: Pretty Terrific If You Live in Hawaii or Massachusetts
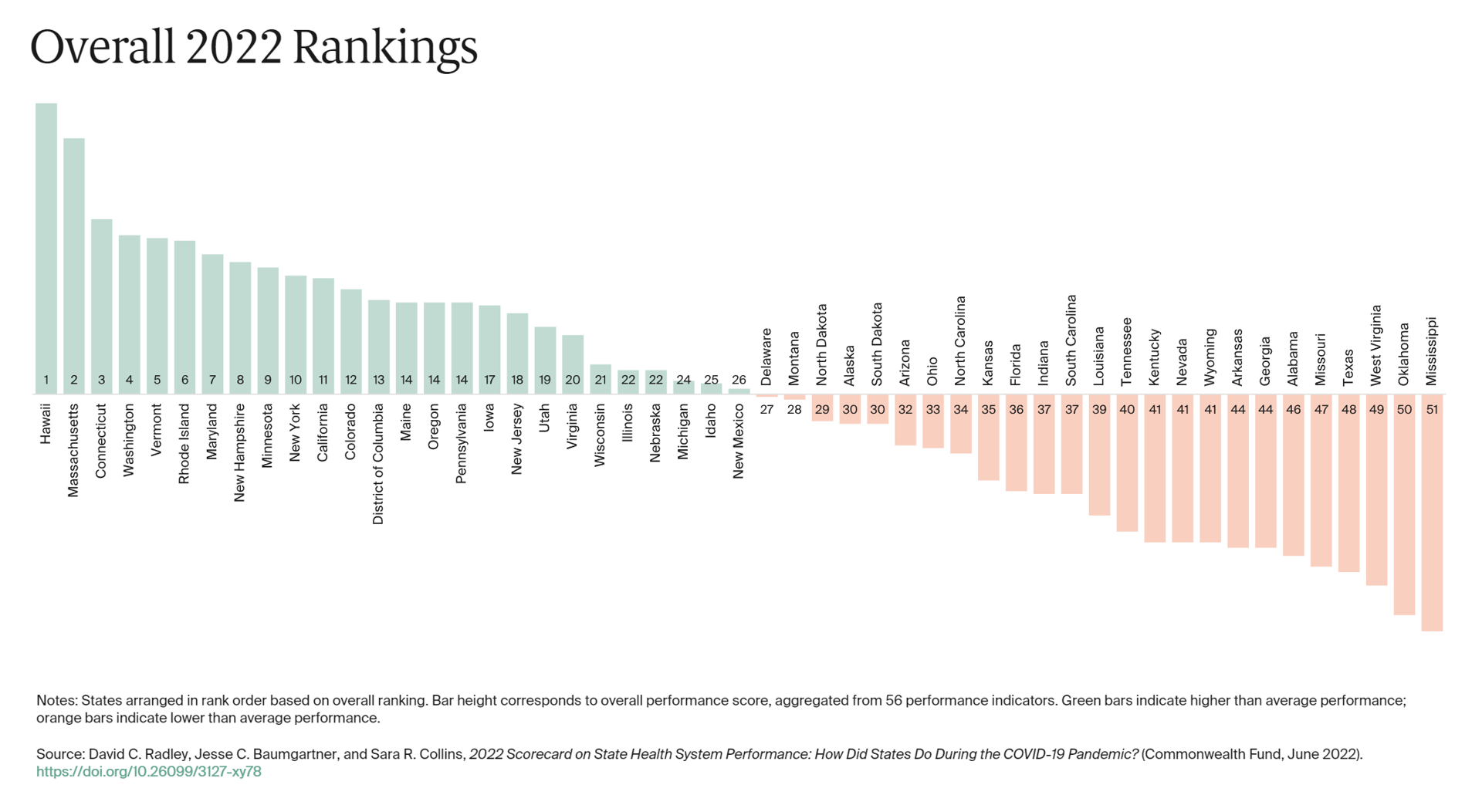
The best U.S. states to live in for health and health care are Hawaii, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Washington, Vermont, Rhode Island, and Maryland… Those are the top health system rankings in the new 2022 Scorecard on State Health System Performance annual report from the Commonwealth Fund. If you live in Mississippi, Oklahoma, West Virginia, Texas, Missouri, Alabama, Georgia, or Arkansas, your health care and outcomes are less likely to be top-notch, the Fund’s research concluded. The Commonwealth Fund has conducted this study since 2006, assessing a range
Doximity Study Finds Telehealth Is Health for Every Day Care
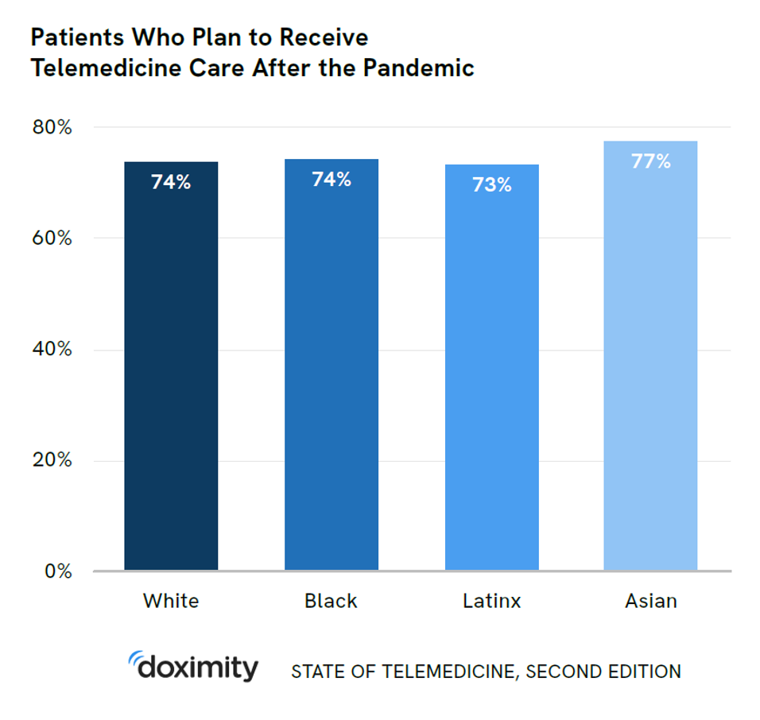
There’s more evidence that doctors and patients, both, want to use telehealth after the COVID-19 pandemic fades. Doximity’s second report on telemedicine explores both physicians’ and patients’ views on virtual care, finding most doctors and health consumers on the same page of virtual care adoption. For the physicians’ profile, Doximity examined 180,000 doctors’ who billed Medicare for telemedicine claims between January 2020 and June 2021. Telemedicine use did not vary much across physician age groups. Doctors in specialties that manage chronic illnesses were more likely to use telehealth: endocrinology (think: diabetes), gastroenterology, rheumatology, urology, nephrology, cardiology, ENT, neurology, allergy, and
The 2021 Shkreli Awards: Lown Institute Counts Down the Top 10 Healthcare Industry Abuses in the Coronavirus Pandemic

The first year of the coronavirus pandemic in America was a kind of stress test on the U.S. health care system, revealing weak links and opportunities for bad behavior. “These are not just about individual instances or bad apples,” Dr. Vikas Saini, President of The Lown Institute, explained, referring to them as “cautionary tales” of the current state of U.S. health care. Dr. Saini and his colleague Shannon Brownlee released the annual Lown Institute 2020 Shkreli Awards this week, highlighting their ten most egregious examples of the worst events in U.S. health care that happened in the past year —
Telehealth Use Among Older Americans: Growing Interest, Remaining Concerns
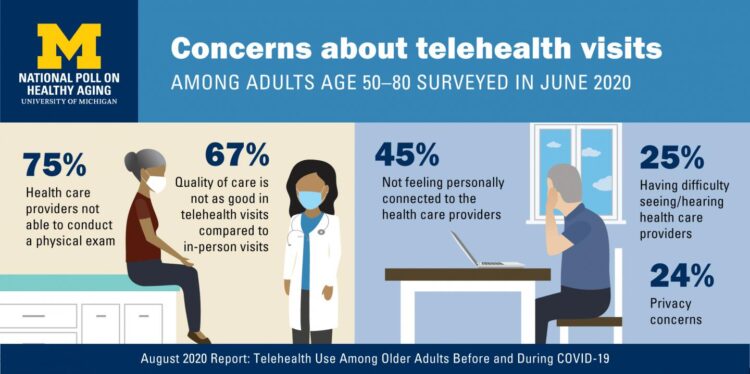
In the Fear of Going Out Era spawned by the COVID-19 pandemic, many patients were loath to go to the doctor’s office for medical care, and even less keen on entering a hospital clinic’s doors. This drove health consumers to virtual care platforms in the first months of the public health crisis — including lots of older people who had never used telemedicine or even a mobile health app. In the August 2020 National Poll on Heathy Aging, the University of Michigan research team found a 26% increase in telehealth visits from 2019 to 2020, March to June 2020 year-over-year.
An Airline, A Hospital and A Disinfectant Brand Walk Into A(n Airport) Bar–the New Health/Care Collaboration in the Age of COVID

You’ve heard the one about three characters walking into a bar. A new collaboration between United Airlines, Cleveland Clinic and Clorox reminded me of that scenario, and that in the age of the coronavirus pandemic, collaboration can bolster our health. In the era of COVID-19, people — consumers. patients managing chronic conditions, and caregivers (whether for younger or older loved ones) — are concerned about contracting the virus. In U.S. states where governors mandated shelter-at-home for much of the first half of 2020, millions of people have become conditioned to physically distance, wear face coverings, and #StayHome. In particular, workers
Retail Pricing in U.S. Health Care? Why Transparency Is Hard to Do

“It’s the prices stupid,” Uwe Reinhardt and Gerard Anderson and colleagues asserted in the title their seminal Health Affairs manifesto on U.S. healthcare spending. Sixteen years later, yesterday on 8th July 2019, a Federal U.S. judge blocked, in the literal last-minute, a DHHS order mandating prescription drug companies to publish “retail prices” of medicines in direct-to-consumer TV ads. I was getting this post on transparency together just before that announcement hit the press, so this post would have had a different nuance yesterday compared with today. And that’s how health care politics and economics in America roll these days. Welcome to
Medical Costs Are Consuming Americans’ Financial Health
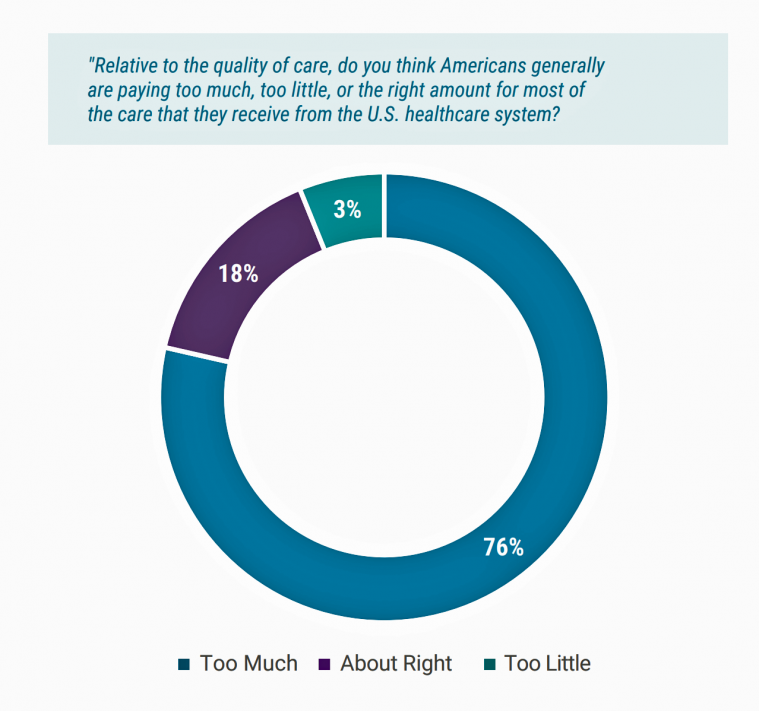
Spending on medical care costs crowded out other household spending for millions of Americans in 2018, based on The U.S. Healthcare Cost Crisis, a survey from West Health and Gallup. Gallup polled 3,537 U.S. adults 18 and over in January and February 2019. One in three Americans overall are concerned they won’t be able to pay for health care services or prescription drugs: that includes 35% of people who are insured, and 63% of those who do not have insurance. Americans borrowed $88 billion in 2018 to pay for health care spending, West Health and Gallup estimated. 27 million Americans
Patients, Health Consumers, People, Citizens: Who Are We In America?

“Patients as Consumers” is the theme of the Health Affairs issue for March 2019. Research published in this trustworthy health policy publication covers a wide range of perspectives, including the promise of patients’ engagement with data to drive health outcomes, citizen science and participatory research where patients crowdsource cures, the results of financial incentives in value-based plans to drive health care “shopping” and decision making, and ultimately, whether the concept of patients-as-consumers is useful or even appropriate. Health care consumerism is a central focus in my work, and so it’s no surprise that I’ve consumed every bit of this publication. [In
The Health of A Nation – Being Healthy In America Depends on Where You Live

In the US, when it comes to life and death, it’s good to live in Hawaii, Utah, Minnesota, North Dakota, and Iowa — the top five states with the greatest life expectancy and healthy life expectancy at birth in 2016. For health and longevity, sorry to see the lowest five ranked states are Washington DC which ranks last, along with Mississippi, Louisiana, South Carolina, and Alabama. This sober geography-is-health-destiny update was published this week in JAMA, The State of US Health, 1990-2016: Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Among US States. The first chart illustrates states down the left
Add Behavioral Data to Social Determinants For Better Patient Understanding
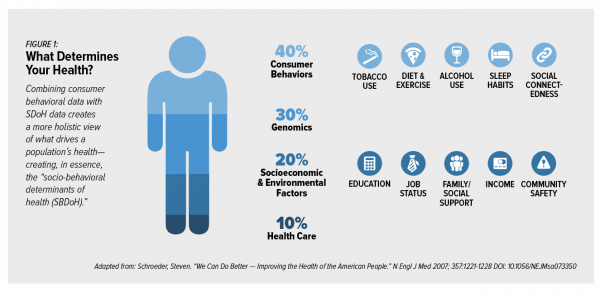
“Health agencies will have to become at least as sophisticated as other consumer/retail industries in analyzing a variety of data that helps uncover root causes of human behavior,” Gartner recommended in 2017. That’s because “health” is not all pre-determined by our parent-given genetics. Health is determined by many factors in our own hands, and in forces around us: physical environment, built environment, and public policy. These are the social determinants of health, but knowing them even for the N of 1 patient isn’t quite enough to help the healthcare industry move the needle on outcomes and costs. We need to
Building Trust and Truth in Patient Social Networks
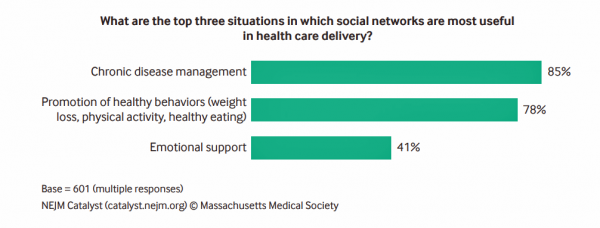
We are only just past the dawn of the second machine age, where digitization is enabling artificial intelligence. “Our new tools are destroying both trust and truth, creating a hunger for community and authenticity. We crave actual physical connection to neighbours, colleagues, and fellow townspeople, even if digitally facilitated.” Anne-Marie Slaughter wrote this in a column I read this morning in the Financial Times titled, “Our struggle with technology to protect trust and truth.” Trust and truth underpin health engagement, we learned in the first Edelman Health Engagement Barometer launched ten years ago. Those were the early days of the formation
The United States of Care Launches to Promote Healthcare for All of US

Let’s change the conversation and put healthcare over politics. Sounds just right, doesn’t it? If you’re reading Health Populi, then you’re keen on health policy, health economics, most of all, patients: now playing starring roles as consumers, caregivers, and payors in their own care. Andy Slavitt, former Acting Administrator of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), has assembled a diverse group of health care leaders who care about those patients/people, too, appropriately named the United States of Care. Founders include Dr. Bill Frist, former Republican U.S. Senator from Tennessee, Dave Durenberger, former Republican U.S. Senator from Minnesota, and
Healthcare Overtreatment in the U.S. – Risky and Costly
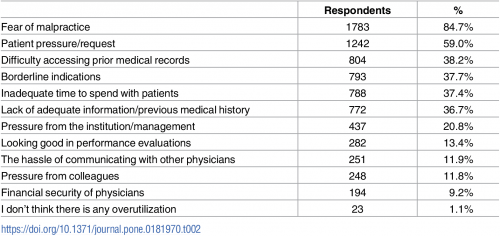
Overtreatment is a major contributor to waste and patient risk in America. Most U.S. physicians say it’s a common fact of life in American healthcare, gleaned through physician survey detailed in Overtreatment in the United States, published in PLOS One on September 6, 2017. The overwhelming majority (8 in 10 physicians) identified malpractice as the reason for overtreatment, followed by patient pressure/request (59%). Other reasons cited for overtreatment included: Difficulty accessing prior medical records Borderline indications Inadequate time to spend with patients, and Lack of adequate information or previous medical history. Overall, physicians judged 20% of healthcare to fall into
Healthcare Quality and Access Disparities Persist in the U.S.
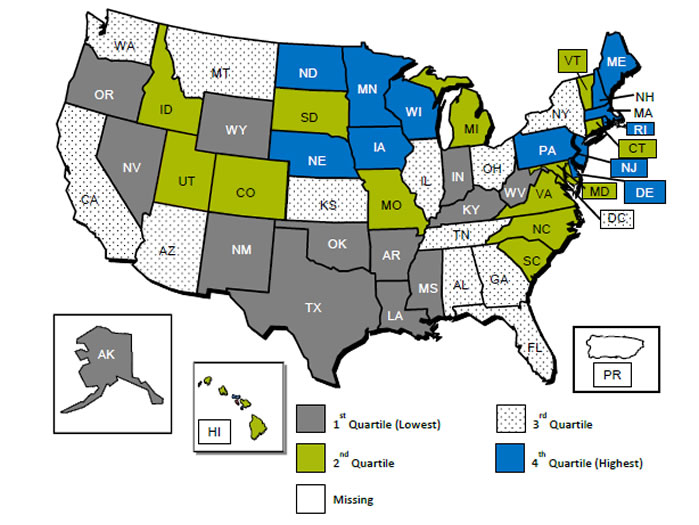
In 2015, poor and low-income people in America had worse health care than high-income households; care for nearly half of the middle-class was also worse than for wealthier families. Welcome to the 2016 National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). The report assesses many measures quantifying peoples’ access to health care, such as uninsurance rates (which improved between 2010 and 2016), and quality of health care — including person-centered care, patient safety, healthy living, effective treatment, care coordination, and care affordability. While some disparities lessened between 2000 and 2015, disparities
The Pursuit of Health Equity and the State of U.S. Health Care
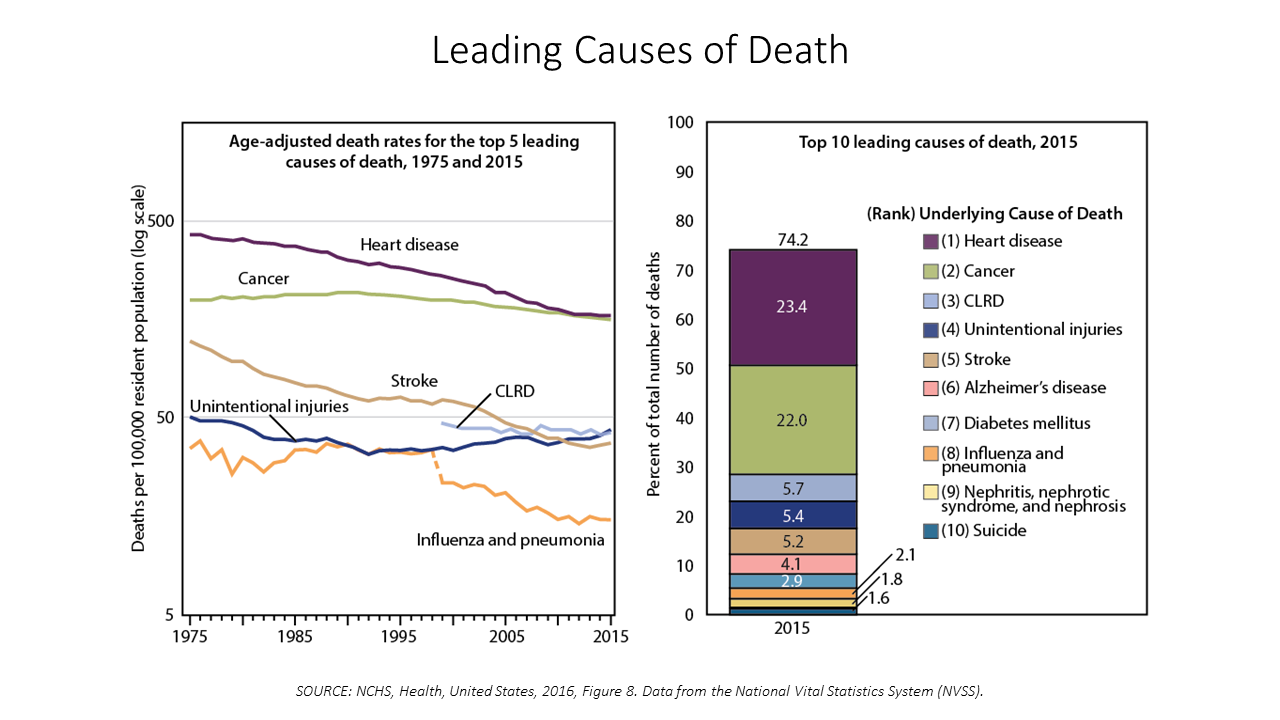
Between 2014 and 2015, death rates increased for eight of the ten leading causes; only death rates caused by cancer fell, and mortality rates for influenza and pneumonia stayed flat. The first chart paints this sobering portrait of Americans’ health outcomes, presented in the CDC’s data-rich 488-page primer, Health, United States, 2016. Think of this publication as America’s annual report on health. Every year, it is prepared and submitted to the President and Congress by the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services. This year’s report was delivered by DHHS Secretary Tom Price to President Trump and the
Consumer Experience Is An Integral Part of the Healthcare Experience

Patient satisfaction should be baked into healthcare provider service goals, according to Prioritizing the Patient Experience from West Corporation, the communications company. West is in the business of improving communications systems, and has a vested interest in expanding comms in health. This research polled patients and providers to assess how each healthcare stakeholder perceives various patient satisfaction issues, which when done well are grounded in sound communications strategy and technologies. Patient satisfaction is directly linked to the bottom lines of healthcare organizations, West contends, due to two key drivers: Evolving payment models are increasingly tying patient satisfaction to reimbursements; and,
Financial Stress As A Health Risk Factor Impacts More Americans
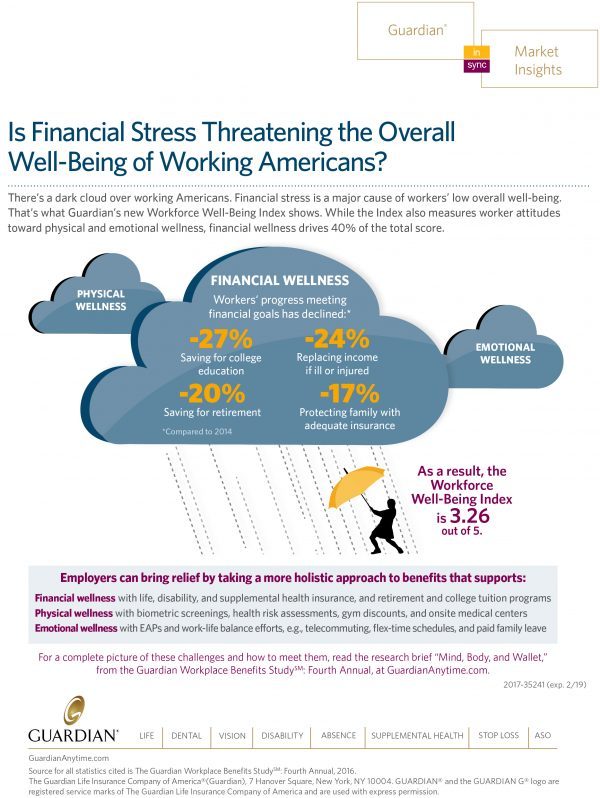
A family in Orange County, California, paid a brother’s 1982 hospital bill by selling 50 pieces of their newly-deceased mother’s jewelry. “It’s what she wanted,” the surviving son told a reporter from The Orange County Register. The cache of jewelry fetched enough to pay the $10,000 bill. Patients in the U.S. cobble together various strategies to pay for healthcare, as the first chart drawn from a Kaiser Family Foundation report on medical debt attests. As health care consumers, people cut back on household spending like vacations and household goods. Two-thirds of insured patients use up all or most of their savings
Consumer Healthcare Reviews on Yelp Help
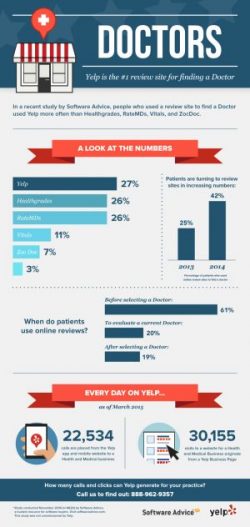
Just as consumers use TripAdvisor, Zagat, OpenTable, and their Facebook pages to review restaurants, hotels, automobiles, and financial services companies, many patients – now health consumers in earnest – have taken to reviewing healthcare services in social networks. Finding reliable, understandable information about healthcare quality and prices is very challenging for most consumers. Are healthcare reviews on social networks statistically valid? An analysis of consumer ratings for New York State hospitals on Yelp, the social network, were positively correlated to objective scores of hospital quality, according to the research published in Yelp for Health: Using the Wisdom of Crowds to
1 in 3 Americans Still Self-Rations Healthcare
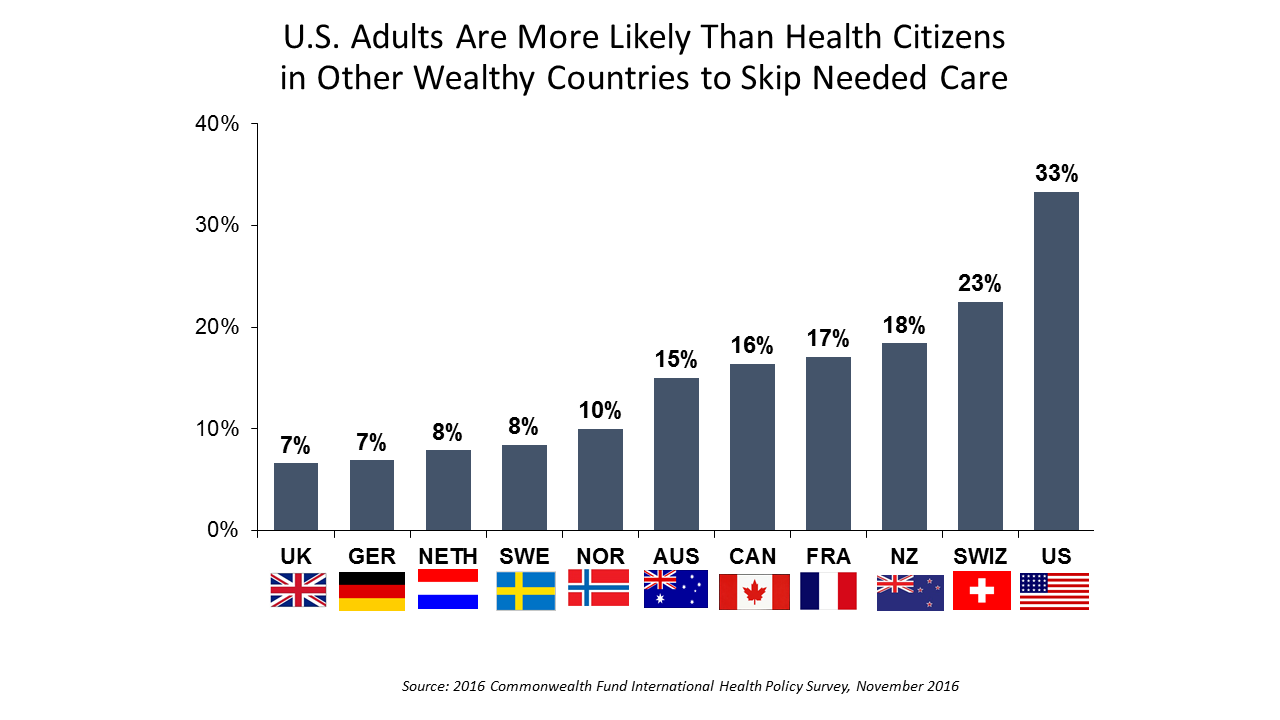
People in the U.S. are much more likely to go without health care they need compared with health citizens in 10 other wealthy countries, according to the Commonwealth Fund’s 2016 international survey. One-third of Americans did not seek care due to costs, including going without recommended care, failing to fill a prescription drug, and/or not seeing a doctor when sick. While this self-rationing proportion of Americans dropped from 37% in 2013, the U.S. still ranks #1 in foregoing necessary healthcare due to cost. “In comparison to adults in the other 10 countries, adult sin the U.S. are sicker and more
The Promise of the Platform Economy for Health

There’s a lot of talk about the growing platform economy. If well-designed platforms get adopted in healthcare, they may help our ailing healthcare systems get better. The quality, safety, and convenience of healthcare in America suffer from a lack of patients’ personal health data being essentially locked in data siloes. The diagnosis is lack of data “liquidity:” the ability for our health information generated in various touch points in the healthcare system and in our personal lives each day to move outside of the locations where the bits and bytes were first created: to our clinicians, researchers, health providers, and to
Paper and Fax, Not EHRs or Portals, Are Popular for Health Data Sharing
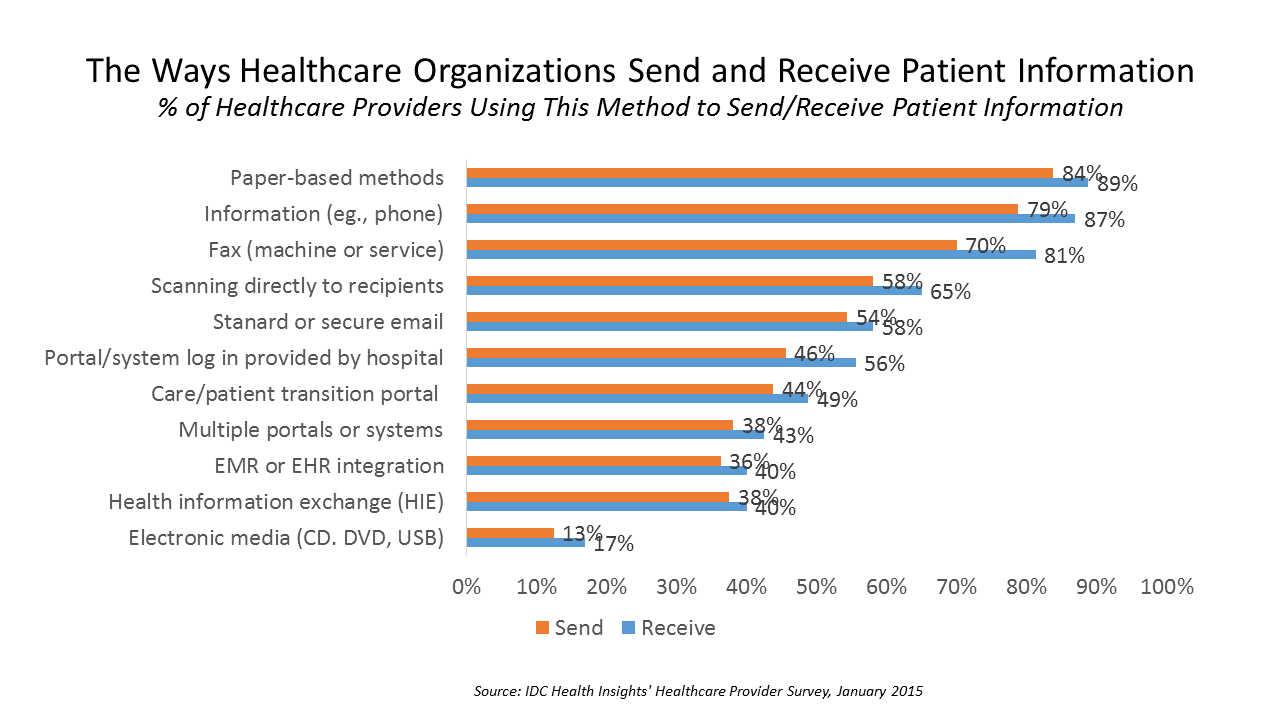
Faxing in health care ranks higher in patient data information sharing than using secure email, online portals, health information exchange (HIE), or leveraging electronic health records. Welcome to the American healthcare system in 2016, as described in a market spotlight published by IDC, The Rocky Road to Information Sharing in the Health System. IDC’s survey research among healthcare providers forecasts the “rocky road” to information sharing. That rocky road is built for medical errors, duplication of services, greater healthcare costs, and continued health il-literacy for many patients. “The holy grail of interoperability — lower-cost, better-quality care with an improved experience for
U.S. Health At A Glance – Not So Healthy
People in the U.S. have lower life expectancy, a growing alcohol drinking problem, and relatively high hospital inpatient rates for chronic conditions compared with other OECD countries. And, the U.S. spends more on health care as a percent of GDP than any other country in the world. This isn’t new-news, but it confirms that U.S. health citizens aren’t getting a decent ROI on health spending compared with health citizens around the developed world. In the OECD’s latest global look at member countries’ health care performance, Health at a Glance 2015, released today, the U.S. comes out not-so-healthy in the context
Consumers trust retailers to manage health as much as health providers
40% of U.S. consumers trust Big Retail to manage their health; 39% of U.S. consumers trust healthcare providers to manage their health. What’s wrong with this picture? The first chart shows the neck-and-neck tie in the horse race for consumer trust in personal health management. The Walmart primary care clinic vs. your doctor. The grocery pharmacy vis-a-vis the hospital or chain pharmacy. Costco compared to the chiropractor. Or Apple, Google, Microsoft, Samsung or UnderArmour, because “digitally-enabled companies” are virtually tied with health providers and large retailers as responsible health care managers. Welcome to The Birth of the Healthcare Consumer according
Doctors who write right: Gawande, Topol and Wachter put people at the center of health/care
There’s a trifecta of books written by three brilliant doctors that, together, provide a roadmap for the 21st century continuum of health care: The Patient Will See You Now by Eric Topol, MD; The Digital Doctor from Robert Wachter, MD; and, Being Mortal, by Atul Gawande. Each book’s take provides a lens, through the eyes of a hands-on healthcare provider, on healthcare delivery today (the good, the warts and all) and solutions based on their unique points-of-view. This triple-review will move, purposefully, from the digitally, technology optimistic “Gutenberg moment” for democratizing medicine per Dr. Topol, to the end-game importance of
Health and financial well-being are strongly linked, CIGNA asks and answers
The modern view on wellness is “having it all” in terms of driving physical, emotional, mental and financial health across one’s life, according to CIGNA’s survey report, Health & Financial Well-Being: How Strong Is the Link? The key elements of whole health, as people define them are: – Absence of sickness, 37% – Feeling of happiness, 32% – Stable mental health, 32% – Management of chronic disease, 15% – Financial health, 14% – Living my dreams, 9%. 1 in 2 people (49%) agree that health and wellness comprise “all of these” elements, listed above. This holistic view of health is
Novel concept: people + health pricing information = market competition
In the post-Recession American economy, people shop for value in all things. And that includes health care services like MRIs — when patients are informed of pricing differences among imaging facilities and given free rein to pick-and-choose among them. In addition to lowering imaging costs in a community, price transparency also generated competition between providers. Health Affairs published this research detailed in Price Transparency for MRIs Increased Use of Less Costly Providers And Triggered Provider Competition in August 2014. An Economics 101 course teaches us that a well-oiled (perfect) market depends on lots of sellers of a product and lots of
The Season of Healthcare Transparency – Chaos, then Creation, Part 5
The consumer demand side for healthcare transparency is hungry for the light to shine on health care costs, quality and information that’s relevant and meaningful to the individual. The supply side is fast-growing, with websites and portals, government-sponsored projects, commercial-driven start-ups, and numerous mobile apps. These tools endeavor to: Help people find and access services Schedule appointments Compare peer consumers’ reviews for those providers Calculate and prepare for out-of-pocket co-payments deriving from their health plan Negotiate prices with providers Pay for the services, and Reconcile the payment with a high-deductible health plan or health savings account. On the demand side, consumers
The Season of Healthcare Transparency – HFMA’s Price Transparency Manifesto – Part 1
As Big Payors continue to shift more costs onto health consumers in the U.S., the importance of and need for transparency grows. 39% of large employers offered consumer-directed health plans (CDHPs) in 2013, and by 2016, 64% of large employers plan to offer CDHPs. These plans require members to pay first-dollar, out-of-pocket, to reach the agreed deductible, and at the same time manage a health savings account (HSA). In the past several weeks, many reports have published on the subject and several tools to promote consumer engagement in health finance have made announcements. This week of posts provides an update on
HIMSS14 Monday Morning Quarterback – The Key Takeaways
Returning to terra firma following last week’s convening of the 2014 annual HIMSS conference…taking some time off for family, a funeral, the Oscars, and dealing with yet another snowstorm…I now take a fresh look back at #HIMSS14 at key messages. In random order, the syntheses are: Healthcare in America has entered an era of doing more, with less...and health information technology is a strategic investment for doing so. The operational beacon going forward is moving toward The Triple Aim: building population health, enhancing the patient’s experience, and lowering costs per patient. The CEO of Aetna, Mark Bertolini, spoke of the
Innovating and thriving in value-based health – collaboration required
In health care, when money is tight, labor inputs like nurses and doctors stretched, and patients wanting to be treated like beloved Amazon consumers, what do you do? Why, innovate and thrive. This audacious Holy Grail was the topic for a panel II moderated today at the Connected Health Symposium, sponsored by Partners Heathcare, the Boston health system that includes Harvard’s hospitals and other blue chip health providers around the region. My panelists were 3 health ecosystem players who were not your typical discussants at this sort of meeting: none wore bow ties, and all were very entrepreneurial: Jeremy Delinsky
Consumers don’t get as much satisfaction with high-deductible health plans
Since the advent of the so-called consumer-directed health care era in the mid-2000s, there’s been a love-gap between health plan members of traditional plans, living in Health Plan World 1.0, and people enrolled in newer consumer-driven plans – high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) and consumer-directed health plans (CDHPs). That gap in plan satisfaction continues, according to the Employee Benefits Research Institute (EBRI)’s poll of Americans’ consumer engagement in health care. The survey was conducted with the Commonwealth Fund. As the bar chart illustrates, some 62% of members in traditional plans were satisfied (very or extremely) with their health insurance in 2012.
The health care automat – Help Yourself to healthcare via online marketplaces
Imagine walking into a storefront where you can shop for an arthroscopy procedure, mammogram, or appointment with a primary care doctor based on price, availability, quality, and other consumers’ opinions? Welcome to the “health care automat,” the online healthcare marketplace. This is a separate concept from the new Health Insurance Marketplace, or Exchange. This emerging way to shop for and access health care services is explored in my latest paper for the California HealthCare Foundation (CHCF), Help Yourself: The Rise of Online Healthcare Marketplaces. What’s driving this new wrinkle in retail health care are: U.S. health citizens morphing into consumers,
10 Reasons Why ObamaCare is Good for US
When Secretary Sebelius calls, I listen. It’s a sort of “Help Wanted” ad from the Secretary of Health and Human Services Kathleen Sebelius that prompted me to write this post. The Secretary called for female bloggers to talk about the benefits of The Affordable Care Act last week when she spoke in Chicago at the BlogHer conference. Secretary Sebelius’s request was discussed in this story from the Associated Press published July 25, 2013. “I bet you more people could tell you the name of the new prince of England than could tell you that the health market opens October 1st,” the
Bending the cost-curve: a proposal from some Old School bipartisans
Strange political bedfellows have come together to draft a formula for dealing with spiraling health care costs in the U.S. iin A Bipartisan Rx for Patient-Centered Care and System-Wide Cost Containment from the Bipartisan Policy Center (BPC). The BPC was founded by Senate Majority Leaders Howard Baker, Tom Daschle, Bob Dole, and George Mitchell. This report also involved Bill Frist, Pete Domenici, and former White House and Congressional Budget Office Director Dr. Alice Rivlin who together work with the Health Care Cost Containment Initiative at the BPC. The essence of the 132-page report is that the U.S. health system is
Let patients help: the BMJ covers an American ePatient’s learnings
In this week’s BMJ (British Medical Journal), an American patient tells his story about being equipped, enabled, empowered and engaged — the many “e’s” making up the prefix of “ePatient.” This definition comes out of the work of Dr. Tom Ferguson, who worked with the e-Patient Scholars Working Group in 2007, to publish the first white paper about the phenomenon, e-Patients: how they can help us heal health care. ePatient Dave is the patient-author of the BMJ piece, making the case for shared decision-making and patient involvement in health care decisions. He writes in the conclusion, “The value delivered by skilled
The need for a Zagat and TripAdvisor in health care
Patient satisfaction survey scores have begun to directly impact Medicare payment for health providers. Health plan members are morphing into health consumers spending “real money” in high-deductible health plans. Newly-diagnosed patients with chronic conditions look online for information to sort out whether a generic drug is equivalent to a branded Rx that costs five-times the out-of-pocket cost of the cheaper substitute. While health care report cards have been around for many years, consumers’ need to get their arms around relevant and accessible information on quality and value is driving a new market for a Yelp, Travelocity, or Zagat in
Most consumers will look to health insurance exchanges to buy individual plans in 2013
As the Affordable Care Act, health reform, aka Obamacare, rolls out in 2013, American health insurance shoppers will look for sources of information they can trust on health plan quality and customer service satisfaction — as they do for automobiles, mobile phone plans, and washing machines. For many years, one of a handful of trusted sources for such insights has been J.D. Power and Associates. J.D. Power released its 2013 Member Health Plan Study (the seventh annual survey) and found that most consumers currently enrolled in a health plan have had a choice of only “one” at the time
Bill Clinton’s public health, cost-bending message thrills health IT folks at HIMSS
In 2010, the folks who supported health care reform were massacred by the polls, Bill Clinton told a rapt audience of thousands at HIMSS13 yesterday. In 2012, the folks who were against health care reform were similarly rejected. President Clinton gave the keynote speech at the annual HIMSS conference on March 6, 2013, and by the spillover, standing-room-only crowd in the largest hall at the New Orleans Convention Center, Clinton was a rock star. Proof: with still nearly an hour to go before his 1 pm speech, the auditorium was already full with only a few seats left in the
Health consumers don’t understand overtreatment, and their role in driving health costs
Overuse of health care is defined as the delivery of health care services for which the risks outweigh the benefits, according to a study into the utilization of ambulatory care health services published in the January 28, 2013, issue of JAMA Internal Medicine (the new title for the Archives of Internal Medicine). “Trends in the Overuse of Ambulatory Health Care Services in the United States” found that, of the estimated $700 billion that is wasted annually in U.S. health care, overuse comprises about $280 billion – over one-third of waste — equal to over 10% of total health spending in
Living paycheck to paycheck: what it means for health
While 50% of Americans feel they have a sound financial position, the other half is living paycheck to paycheck. 8% say they can’t even pay for essentials. The second annual Allstate “Life Tracks” Poll finds American adults split between have’s and have not’s, with even the “have’s” feeling less than financially literate. There is an equal split between people who feel they’re in an “excellent” or “good” financial position compared with those who feel they’re in financially “fair” or “poor” shape. Men feel more financially secure than women; 3 in 4 single parents feel less well-off compared to the average
Employees will bear more health costs to 2017 – certainty in an uncertain future
Amidst uncertainties and wild cards about health care’s future in the U.S., there’s one certainty forecasters and marketers should incorporate into their scenarios: consumers will bear more costs and more responsibility for decision making. The 2012 Deloitte Survey of U.S. Employers finds them, mostly, planning to subsidize health benefits for workers over the next few years, while placing greater financial and clinical burdens on the insured and moving more quickly toward high-deductible health plans and consumer-directed plans. In addition, wellness, prevention and targeted population health programs will be adopted by most employers staying in the health care game, shown in
Said the EHR to the doctor, “you like me, you really like me!”
Over one-half of office-based physicians in the U.S. had adopted an electronic health record (EHR) in 2011. Among theese adopters, 85% were satisfied: 38% “very,” and 47% “somewhat.” Those are pretty good reviews considering so many came to EHRs based on the government’s HITECH incentive and not motivated purely out of intrinsic personal passion to adopt digital medical records systems. This update comes from the July 2012 Data Brief from the National Center for Health Statistic, Physician Adoption of Electronic Health Records Systems: United States. 2011. The report details survey findings from 5,232 office-based physicians who completed the mailed questionnaire in
Converging for health care: how collaborating is breaking down silos to achieve the Triple Aim
On Tuesday, 9 July 2012, health industry stakeholders are convening in Philadelphia for the first CONVERGE conference, seeking to ignite conversation across siloed organizations to solve seemingly intractable problems in health care, together. Why “converge?” Because suppliers, providers, payers, health plans, and consumers have been fragmented for far too long based on arcane incentives that cause the U.S. health system to be stuck in a Rube Goldbergian knot of inefficiency, ineffectiveness and fragmentation of access….not to mention cost increases leading us to devote nearly one-fifth of national GDP on health care at a cost of nearly $3 trillion…and going up.
Why we now need primary care, everywhere
With the stunning Supreme Court 5-4 majority decision to uphold the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA), there’s a Roberts’ Rules of (Health Reform) Order that calls for liberating primary care beyond the doctors’ office. That’s because a strategic underpinning of the ACA is akin to President Herbert Hoover’s proverbial “chicken in every pot:” for President Obama, the pronouncement is something like, “a medical home for every American.” But insurance for all doesn’t equate to access: because 32-some million U.S. health citizens buy into health insurance plans doesn’t guarantee every one of them access to a doctor. There’s a
58% of Americans self-rationing health care due to cost
Since the advent of the Great Recession of 2008, more Americans have been splitting pills, postponing needed visits to doctors, skipping dental care, and avoiding recommended medical tests due to the cost of those health care services. Call it health care self-rationing: the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF) has been tracking this trend for the past several years, and the proportion of American adults rationing health demand is up to 58%. This KFF Health Tracking Poll interviewed 1,218 U.S. adults age 18 and older via landline and cell phone in May 2012. As the chart illustrates, 38% of people are “DIYing” health care
Improving health care through Big Data: a meeting of the minds at SAS
Some 500 data analytics gurus representing the health care ecosystem including hospitals, physician practices, life science companies, academia and consulting came together on the lush campus of SAS in Cary, North Carolina, this week to discuss how Big Data could solve health care’s Triple Aim, as coined by keynote speaker Dr. Donald Berwick: improve the care experience, improve health outcomes, and reduce costs. Before Dr. Berwick, appointed as President Obama’s first head of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Clayton Christensen of the Harvard Business School, godfather of the theory of disruptive innovation in business, spokee about his journey
It’s the prices and the technology, stupid: why U.S. health costs are higher than anywhere in the world
The price of physician services, proliferation of clinical technology and the cost of obesity are the key drivers of higher health spending in the U.S., according to The Commonwealth Fund‘s latest analysis in their Issues of International Health Policy titled, Explaining High Health Care Spending in the United States: An International Comparison of Supply, Utilization, Prices, and Quality, published in May 2012. The U.S. devotes 17.4% of the national economy to health spending, amounting to about $8,000 per person. The UK devotes about 10%, Germany 11.6%, France, 11.8%, Australia 8.7%, and Japan, 8.5%. On the physician pay front, primary care
A $132 doctor’s visit in Hanoi, Vietnam: a diagnosis, value-based health care and a new friend
$132 won’t go far in a U.S. emergency room, but in Vietnam, it gets you first class treatment, a highly-trained and empathetic French doctor, and cheap prescriptions, as well. You could call it Presidential treatment, as a certificate from the White House was proudly displayed in the lobby waiting area sent in appreciation of great care received by President George W. Bush. After arriving in Hanoi two nights ago, following three airline flights over nearly 24 hours, our daughter developed a rough cough that gave her chest pains. We gave the condition one day to improve and then spoke with
Patient engagement and medical homes – core drivers of a high-performing health system
It was Dr. Charles Safran who said, “Patients are the most under-utilized resource in the U.S. health system,” which he testified to Congress in 2004. Seven years later, patients are still under-utilized, not just in the U.S. but around the world. Yet, “when patients have an active role in their own health care, the quality of their care, and of their care experience improves,” assert researchers from The Commonwealth Fund in their analysis of 2011 global health consumer survey data published in the April/June 2010 issue of the Journal of Ambulatory Care Management. This analysis is summarized in International Perspectives on
From volume to value: how health execs see the future of health care
Transparency and authenticity, constant and clear communication, and a drive toward value underpin the future health system — for those health leaders who can commit to these pillars of transformational change. Leading Through Transformation: Top Healthcare CEOs’ Perspectives on the Future of Healthcare summarizes the interaction among 17 health execs who convened at the second CEO Forum held by Huron Healthcare Group. The report was released in January 2012. Health leaders concur that regardless of the politics of the Affordable Care Act and its prospects for whole or partial survival beyond November 2012, market pressures in the health sector are driving
The average annual health costs for a U.S. family of four approach $20,000, with employees bearing 40%
Health care costs have doubled in less than nine years for the typical American family of four covered by a preferred provider health plan (PPO). In 2011, that health cost is nearly $20,000; in 2002, it was $9,235, as measured by the 2011 Milliman Medical Index (MMI). To put this in context, The 2011 poverty level for a family of 4 in the 48 contiguous U.S. states is $22,350 The car buyer could purchase a Mini-Cooper with $20,000 The investor could invest $20K to yield $265,353 at a 9% return-on-investment. The MMI increased 7.3% between 2010 and 2011, about the same
The story of Kaiser Permanente’s EHR
“To call health care’s information management for the most part ‘twentieth century’ is as wrong as calling it ‘twenty-first century;’ it’s nineteenth century,” begins Dr. Donald Berwick, Administrator of the Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services, in the foreword to a new book that tells the story about how the world’s largest health IT project was successfully implemented. Connected for Health was edited by Dr. Louise L. Liang who was senior vice president, Quality and Clinical Systems Support, for the Kaiser Foundation Health Plan and Kaiser Foundation Hospitals between 2002 and 2009. It was during that time that Kaiser envisioned and implemented KP
Choosing doctors in the dark: consumers can’t yet pick docs based on quality
The usual questions a rational health citizen might ask when selecting a physician based on quality aren’t consistently yielding the best choices, according to a study funded by The Commonwealth Fund, Associations Between Physician Characteristics and Quality of Care. Researchers found that individual physician-comparative parameters such as malpractice claims and disciplinary actions, years in practice or medical school ranking had no significant association with better quality performance. Female physicians (vs. male) and Board certification had small significance, 1.6 points and 3.3 points, respectively. This study’s results demonstrate that the metrics consumers assume should be useful proxies for physician quality aren’t as useful
The role of retail health clinics post-health reform
Retail health clinics have served American health consumers for about a decade. What have we learned over these ten years? As retail clinics proliferate the U.S. health care ecosystem, what is their impact on the health system, health consumers, and the health economy? The RAND report, Policy Implications of the Use of Retail Clinics, responds to these issues. The key implications of RAND’s study are that: – Health programs should be designed and paid-for to incorporate the adoption of retail clinics and reduce fragmentation and dis-continuity of care. – Learn from the best practices and patient outcomes gained from
Health reform = meaningful use among health executives
Meeting meaningful use for inpatient EHRs is the top priority among the many challenges health executives face when considering how the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) will impact their organizations. Overall, 2 in 3 health execs place MU for inpatient EHRs as the “highest priority;” among health IT executives, the proportion citing this as the highest priority is 84%. The second-most pressing PPACA priority for health executives is preparing for new models of payment, cited by 17% of health execs overall, and 31% of non-IT executives. CSC surveyed health executives in July to gauge their temperatures on several PPACA line-items including
More money, less effective: the U.S. ranks last again in health system effectiveness
Among seven developed countries – Australia, Canada, Germany, the Netherlands, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and the United States of America — it’s the U.S. that ranks dead last in the effectiveness of the nation’s health system. In particular, the U.S. rates poorly on the issues of coordination of health care, cost-related problems causing access challenges for health citizens, efficiency, equity, and long/healthy/productive lives for citizens. Of course, it also figures in that the U.S. spends more per capita on health care than any other country on the planet: $7,290 per person compared with Health Nation #1, the Netherlands, which
A picture tells a thousand words and health cost disparities in the State of Maine
The Dartmouth Atlas and other health cost analysts have exposed the phenomenon of varying health costs, from the state of Florida to California, Oregon to McAllen, Texas. Now we have evidence of big cost disparities within a relatively small state – the State of Maine. Details on this story appear in the May 16th 2010 Portland Press Herald, which created the illustration shown here based on pricing data collected throughout the state. Health citizens in Maine are fortunate to have a state-funded resource that aggregates and analyzes data on health care cost and quality from health care providers in the state,
Affordable care and better information: what Americans want from a new-and-improved US health system
Anxiety about health care costs tops American citizens’ concerns about health care in the U.S. Rich, poor, insured or un-, 2 in 3 Americans worry about the affordability of health care in America. So it follows, then, that among those without health insurance, 57% blame their uninsured state on the fact that they simply cannot afford it, as shown in the table on the right. Beyond this group, 30% of the uninsured cite the employer’s role in health insurance: 14% aren’t employed, 9% have employers who don’t offer coverage, and 7% are “between jobs.” These findings come from
In the health system popularity contest, the U.S. loses
In this season’s Health System Idol contest, the U.S. loses to most other developed countries. One in three Americans would like to “completely rebuild” the U.S. health system, according to The Harris Poll conducted in ten nations. And another 50% believe that, “fundamental changes are needed to make it work better.” Harris also measured ‘unpopularity’ with another metric: asking whether, “the system works pretty well and only minor changes are necessary.” Adding this yin to the other yang, the mash-up is still the same: the U.S. plays last fiddle to the rest of the world’s health system orchestra.





 Thanks to Jennifer Castenson for
Thanks to Jennifer Castenson for  Jane joined host Dr. Geeta "Dr. G" Nayyar and colleagues to brainstorm the value of vaccines for public and individual health in this challenging environment for health literacy, health politics, and health citizen grievance.
Jane joined host Dr. Geeta "Dr. G" Nayyar and colleagues to brainstorm the value of vaccines for public and individual health in this challenging environment for health literacy, health politics, and health citizen grievance.  I'm grateful to be part of the Duke Corporate Education faculty, sharing perspectives on the future of health care with health and life science companies. Once again, I'll be brainstorming the future of health care with a cohort of executives working in a global pharmaceutical company.
I'm grateful to be part of the Duke Corporate Education faculty, sharing perspectives on the future of health care with health and life science companies. Once again, I'll be brainstorming the future of health care with a cohort of executives working in a global pharmaceutical company.